Wonderful Tips About What Is V In Current Formula
Decoding the 'V' in the Current Formula
1. Understanding the Basics
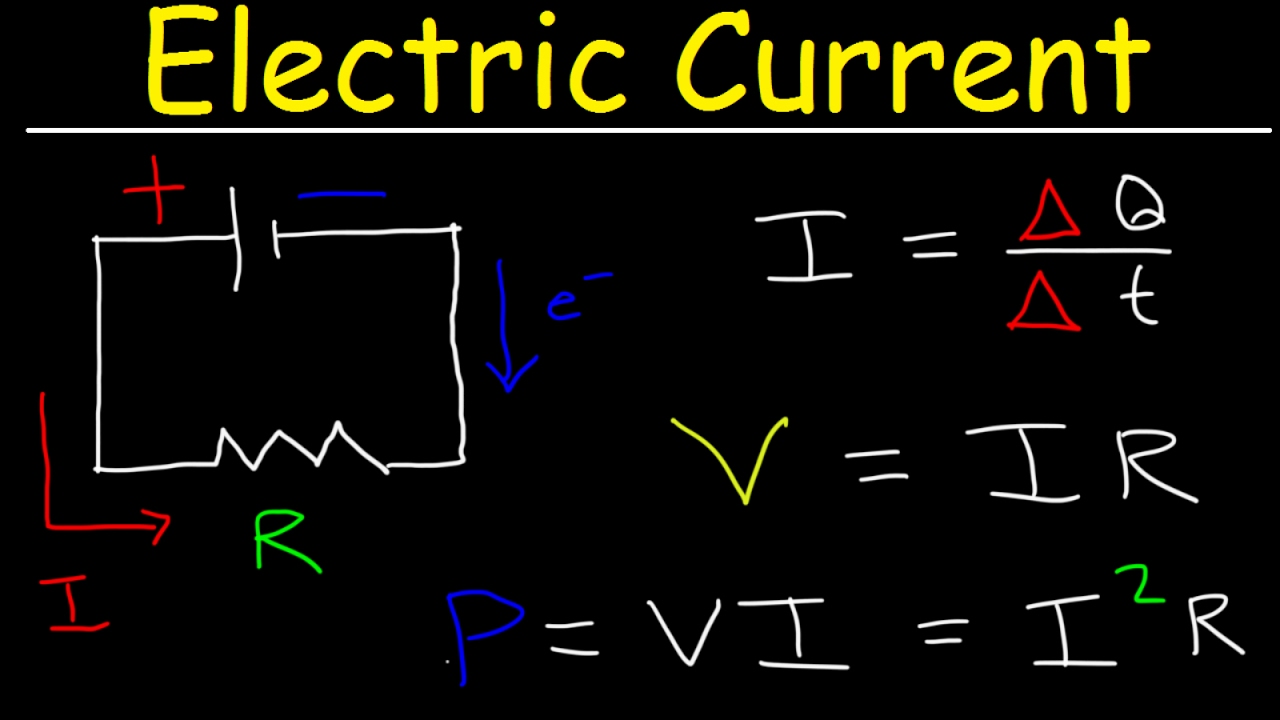
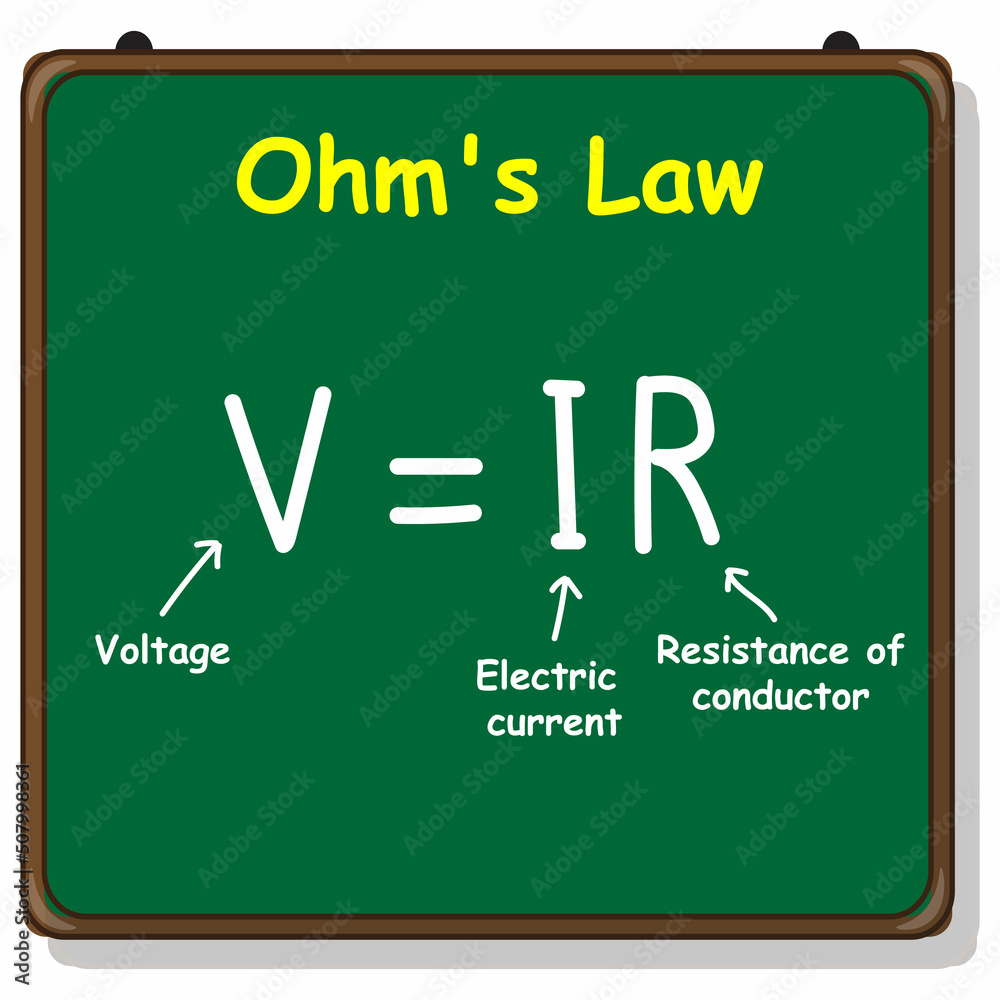
Alright, let's tackle this electrical mystery! When we talk about the "current formula," we usually mean Ohm's Law, which famously states: V = IR. Here, 'V' represents voltage, and it's often measured in volts. But hold on, it's not as simple as just saying "V stands for volts" and calling it a day. Voltage is more than just a number; it's the driving force behind electrical current. Think of it like the pressure in a water pipe; the higher the pressure (voltage), the more water (current) will flow.
Imagine you have a tiny LED light you want to power. If the voltage is too low, the LED won't light up at all. If it's too high, poof — you've got a burnt-out LED. Voltage is the Goldilocks of electricity; you need just the right amount. Its the potential difference between two points in a circuit that allows electricity to do its thing, whether that's lighting a bulb, spinning a motor, or powering your phone.
Now, let's get a little more technical (but not too technical, promise!). Voltage is technically the electrical potential difference. It's the amount of work needed to move a unit charge from one point to another in an electric field. Sounds complicated, right? Well, simply put, its the push that gets the electrons moving. Without voltage, there's no electron movement, and therefore, no current.
So, while 'V' is often simply called 'voltage', remember that it's a measure of electrical potential difference. Its the electrical 'oomph' that makes things happen. Its not just a label; its a critical component in understanding how circuits work and how electricity powers our modern world. And if you ever blow a fuse, you can partially blame the voltage... just kidding (mostly!).
Ohm's Law Formula In Physics. Electric Current Voltage And Resistance
Digging Deeper
2. Beyond Ohm's Law
While 'V' is most commonly associated with voltage in Ohm's Law, it's important to remember that the letter 'V' pops up in other electrical formulas and contexts, too! Sometimes the meaning shifts slightly depending on the situation. For instance, in some advanced circuit analysis problems, 'V' could represent a specific node voltage or a voltage drop across a particular component. The context is everything, like trying to understand a joke without the punchline!
Let's consider alternating current (AC) circuits. Here, voltage isn't a constant value like in direct current (DC) circuits. It's constantly changing, oscillating between positive and negative values. In this case, 'V' might refer to the root mean square (RMS) voltage, which is a way of representing the effective voltage of an AC signal. It's like finding the average height of waves in the ocean; you need to consider the peaks and troughs to get a useful measure.
Another place you might encounter 'V' is in power calculations. Electrical power (P) is related to voltage and current by the formula P = VI. This tells us that the power delivered to a circuit is the product of the voltage and the current. In this context, 'V' still represents voltage, but its role is now tied to determining how much power a device consumes or delivers. It's like knowing how much fuel an engine needs to produce a certain amount of horsepower.
The bottom line is that while the fundamental meaning of 'V' remains as a voltage, always pay attention to the context. Whether it's a basic circuit, an AC system, or a power calculation, understanding the specific role of voltage is key to unlocking the secrets of the equation. It's a versatile symbol with many nuances — kind of like the letter 'V' itself!
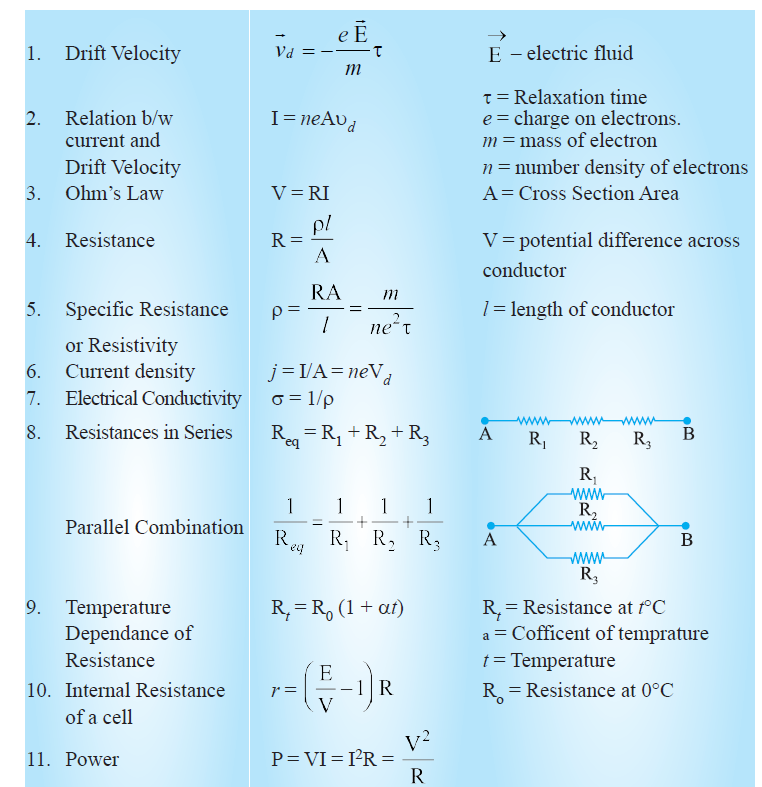
Formula Sheet Of Current Electricity At Eileen Towner Blog
'V' and Electrical Safety
3. Voltage
Let's talk about something serious for a moment: electrical safety. Because while understanding the letter 'V' is interesting, understanding the real-world implications of voltage is crucial for staying safe. High voltage can be extremely dangerous and even fatal. It's not just about getting a little shock; we're talking about potentially life-threatening situations.
Think of voltage as a force — a very powerful force. The higher the voltage, the greater the potential for electrical current to flow through your body. And when that happens, it can disrupt your heart rhythm, damage your nerves, and cause severe burns. That's why it's so important to always take precautions when working with electricity. Always be wary of exposed wires, and do not attempt to mess with electrical systems if you aren't qualified to do so.
One simple but vital safety rule is to always turn off the power before working on any electrical circuit. Use a voltage tester to confirm that the circuit is indeed de-energized. If you're not sure how to do this, consult a qualified electrician. It's always better to be safe than sorry. Electricity is not something to be trifled with; it is a powerful tool, but it must be used with respect.
Another key aspect of electrical safety is understanding the voltage ratings of devices and appliances. Never plug a device into an outlet with a higher voltage than it's designed for. This can cause the device to overheat, catch fire, or even explode. This is especially critical if you are traveling overseas with electric equipment.

Current Formula Power
Measuring 'V'
4. Voltmeter to the Rescue!
So, how do we actually measure this mysterious 'V'? Well, that's where a voltmeter comes in handy! A voltmeter is a device specifically designed to measure voltage between two points in a circuit. It's like a ruler for electricity, telling us the electrical potential difference in volts. Using a voltmeter is actually pretty straightforward, but its important to get the connections right.
To measure voltage, you connect the voltmeter in parallel with the component or circuit you want to measure. This means you connect one lead of the voltmeter to one side of the component and the other lead to the other side. The voltmeter then measures the potential difference between those two points. It's crucial to never connect the voltmeter in series; that's a sure way to damage the meter or the circuit.
There are different types of voltmeters available, from analog meters with a needle to digital meters with a numerical display. Digital voltmeters are generally more accurate and easier to read, but analog meters can sometimes give you a better sense of how the voltage is changing over time. Some multimeters can measure voltage, current and resistance. This makes multimeters very useful in a wide range of situations.
When using a voltmeter, always make sure to select the appropriate voltage range. If you're measuring a voltage of 12 volts, don't select a range of 200 volts; you won't get an accurate reading. Start with a higher range and then gradually decrease it until you get a stable and meaningful reading. Remember to handle the leads of the voltmeter with care, and avoid touching the metal tips while the meter is connected to a live circuit.
FAQs About 'V' and Voltage
5. Your Burning Questions Answered
Let's tackle some common questions about 'V' and voltage that might be swirling around in your brain.
Q: Is voltage the same as current?
A: Absolutely not! Voltage is the electrical potential difference (the 'push'), while current is the flow of electrical charge (the 'water' flowing). They are related by Ohm's Law (V = IR), but they are distinct concepts.Q: What happens if the voltage is too high?
A: Too much voltage can cause devices to overheat, malfunction, or even catch fire. It's crucial to use the correct voltage for your appliances and devices.Q: Can I get shocked by touching a wire with low voltage?
A: Even low voltages can be dangerous, especially if you're in contact with water or other conductive materials. While a low voltage may not be fatal, it can still cause a painful shock. It is important to always stay safe when around electric current!Q: What is the unit of measurement for Voltage?
A: The unit of measurement for Voltage is Volts(V). It indicates the measurement unit.
