Perfect Info About Are Servo Motors AC Or DC

Decoding Servo Motors
Alright, let's get straight to it. You're probably wondering if servo motors are powered by alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). The short answer is: they can be either! But, like many things in the engineering world, the longer, more nuanced answer is a bit more interesting. It depends on the specific type of servo motor and its application. Think of it like asking if a car runs on gas or electricity; both are possible, and each has its advantages.
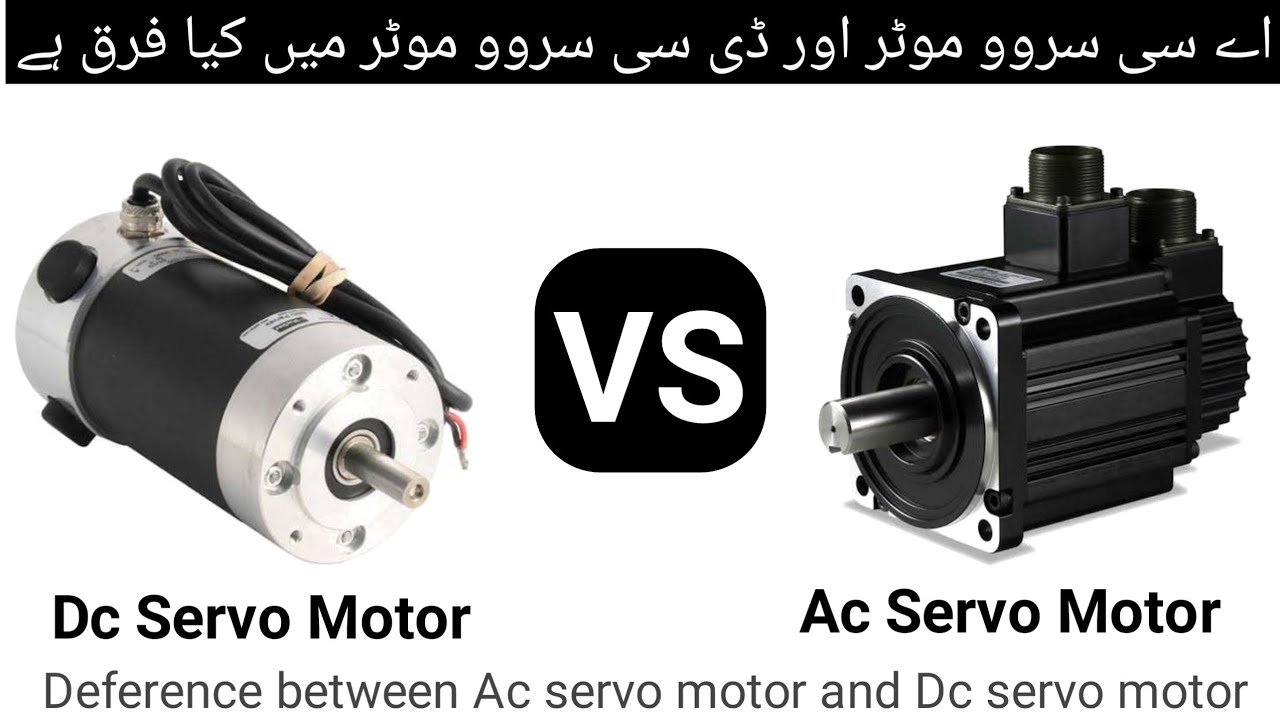
Many smaller, hobbyist-level servo motors, the kind you might find in remote control cars or robotics projects, typically use DC power. These are often simpler in design and control, making them ideal for beginners and applications where precise, low-voltage control is needed. They are readily available and generally more affordable. They're the workhorses of the small-scale automation world.
However, larger, more industrial servo motors often utilize AC power. These beasts are designed for heavy-duty applications, like controlling machinery in factories or operating robotic arms that lift hefty loads. AC servo motors can handle higher voltages and currents, translating to more power and torque. They're the muscle behind the automation revolution in manufacturing.
So, before you go plugging things in, always, always check the motor's specifications! Nobody wants a fried servo motor (or worse!). The label on the motor or its accompanying documentation will clearly state whether it requires AC or DC power. Ignoring this simple step can lead to a rather shocking (pun intended!) and expensive mistake.
1. Which Type Is Right for You? Considering Your Application
Choosing between AC and DC servo motors really boils down to what you need the motor to do. Think about the size of the job, the precision required, and your budget. Are you building a tiny robot that needs to wiggle its toes? DC might be the way to go. Are you controlling a massive industrial arm that needs to precisely weld car parts together? AC is probably your best bet.
DC servo motors are often favored for their simplicity and ease of control. They're generally cheaper to purchase and operate at lower voltages, making them safer for hobbyists and educational settings. They're also readily integrated with microcontrollers, which simplifies the control circuitry. Think Arduino projects and small-scale robotics.
AC servo motors, on the other hand, excel in high-performance applications. They offer greater torque and power, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial machinery. They often incorporate advanced control systems that provide precise positioning and speed control. They're the unsung heroes of modern manufacturing, enabling automated processes with incredible accuracy.
Consider the environment in which the servo motor will operate. DC motors might be more susceptible to wear and tear in harsh environments, while AC motors often have more robust designs. Think about temperature, humidity, and the presence of corrosive materials. A little foresight can save you a lot of headaches (and money) down the road.
9 Practical DC Servo Motor Circuit Diagrams For DIY Projects
Peeking Inside
While the external power source (AC or DC) is important, it's also good to have a basic understanding of what's going on inside a servo motor. Regardless of whether it's AC or DC, a servo motor is a closed-loop system. This means it uses feedback to precisely control its position. A potentiometer or encoder provides feedback to the control circuit, which constantly adjusts the motor's position to match the desired angle.
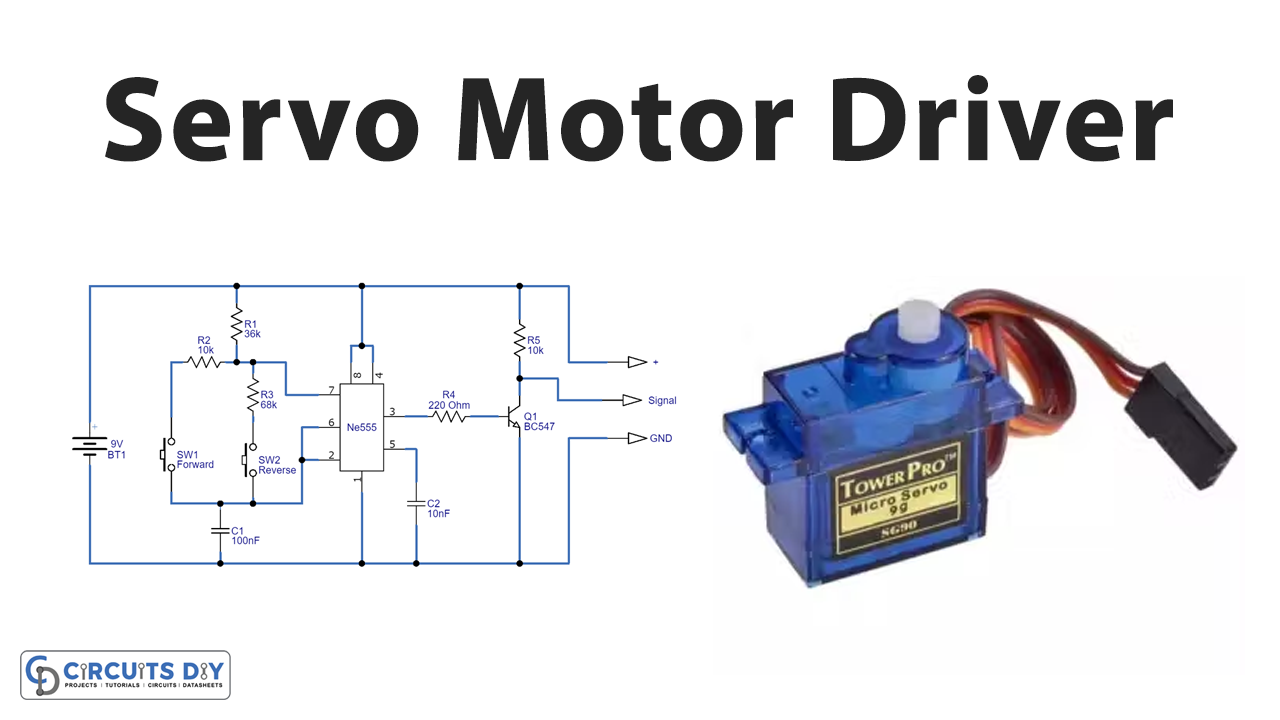
In a DC servo motor, the DC voltage is applied to the motor windings, causing the rotor to spin. The control circuit monitors the position of the rotor via the feedback mechanism and adjusts the voltage to maintain the desired angle. It's a constant dance of adjustment and correction to ensure precise positioning. Simple, elegant, and effective.
AC servo motors operate on a similar principle, but they use AC voltage to drive the motor. The control circuit typically uses a technique called pulse width modulation (PWM) to control the amount of power delivered to the motor. By varying the width of the pulses, the control circuit can precisely control the motor's speed and position. It's like giving the motor tiny bursts of power to nudge it into the right spot.
Both AC and DC servo motors often incorporate gears to increase the torque and reduce the speed. This is especially important for applications where high torque is needed to move heavy loads. The gear ratio determines the trade-off between speed and torque. A higher gear ratio means more torque but lower speed, and vice versa.
2. Digging Deeper
Another important distinction is between brushed and brushless servo motors. This applies to both AC and DC motors. Brushed motors use brushes to make electrical contact with the commutator, which switches the current in the motor windings. Brushless motors, on the other hand, use electronic commutation, which eliminates the need for brushes. This has several advantages.
Brushless servo motors are generally more efficient, reliable, and have a longer lifespan than brushed motors. They also produce less noise and electromagnetic interference. This is because there's no physical contact between the brushes and the commutator, which eliminates wear and tear. They are often the preferred choice for demanding applications where reliability is paramount.
Brushed servo motors are typically cheaper and simpler to manufacture. They are still widely used in many applications, especially where cost is a major factor. However, they require more maintenance due to the wear and tear of the brushes. Think of them as the classic, reliable workhorses of the servo motor world, still getting the job done after all these years.
Choosing between brushed and brushless really depends on your budget and performance requirements. If you need a low-cost, simple solution, a brushed motor might be sufficient. But if you need high performance, reliability, and a long lifespan, a brushless motor is the way to go. Consider the trade-offs and choose wisely.

Common Applications
Servo motors are everywhere! They're the invisible workhorses that power countless devices and machines we use every day. From the mundane to the cutting-edge, servo motors play a crucial role in modern technology.
In robotics, servo motors are used to control the movement of joints, allowing robots to perform complex tasks. They're the muscles and tendons of the robotic world, enabling them to walk, grasp, and manipulate objects with precision. Think about industrial robots welding cars, surgical robots performing delicate procedures, and even robotic vacuum cleaners navigating your living room.
In CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines, servo motors control the movement of cutting tools, allowing them to create intricate shapes and designs. They're the artists of the manufacturing world, transforming raw materials into finished products with incredible accuracy. Think about milling machines, lathes, and 3D printers creating everything from airplane parts to custom-designed jewelry.
In camera systems, servo motors control the pan, tilt, and zoom functions, allowing photographers and videographers to capture stunning images and videos. They're the eyes of the camera, allowing it to see the world from different perspectives. Think about surveillance cameras, robotic cameras in film studios, and even the autofocus system in your smartphone camera.
3. Troubleshooting Tips and Tricks
Even the best servo motors can sometimes run into problems. Here are a few troubleshooting tips to help you diagnose and fix common issues. First, always check the power supply. Make sure the voltage and current are within the motor's specifications. A weak or unstable power supply can cause erratic behavior.
Next, check the wiring connections. Make sure all the wires are securely connected and that there are no loose or frayed wires. A loose connection can cause intermittent problems and can even damage the motor. Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the wires.
If the motor is not responding, check the control signal. Make sure the signal is within the correct range and that it's being properly transmitted to the motor. Use an oscilloscope to visualize the control signal and see if it's clean and stable.
Finally, check the motor for physical damage. Look for any cracks, dents, or other signs of damage. If the motor is physically damaged, it may need to be replaced. Regular maintenance and careful handling can help prevent physical damage.

Types Of Servo Motors
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
4. Q
A: Absolutely not! Directly connecting a DC servo motor to an AC power supply will likely damage the motor beyond repair. You need a DC power supply with the correct voltage and current rating for your specific motor.
5. Q
A: Overloading a servo motor can cause it to overheat, stall, or even burn out. The motor may also lose its position accuracy or become erratic. Always choose a motor that is appropriately sized for the load it will be carrying.
6. Q
A: Consider the torque, speed, precision, and power requirements of your application. Also, think about the size, weight, and environmental conditions. Read the motor's specifications carefully and choose a motor that meets your needs.
7. Q
A: While most servo motors are designed for either AC or DC, some specialized servo drives can accept a wide range of input voltages, including both AC and DC. These drives internally convert the input voltage to the appropriate voltage for the motor.