Glory Info About Is RS-422 Full-duplex

FTDIFT232RLCHIPUSBTORS422FULLDUPLEX9CORE9PINWEWIREEND
Decoding RS-422
1. What Exactly is RS-422 Anyway?
Alright, let's dive into the world of RS-422. No, it's not a new kind of robot from a sci-fi movie. It's actually a standard for serial communication. Think of it as a specific way devices "talk" to each other using wires. It's been around for quite a while, and it's known for being reliable, especially over longer distances compared to some of its counterparts, like RS-232. Imagine trying to shout across a football field versus whispering RS-422 is like having a megaphone, ensuring your message gets through loud and clear (or, at least, with minimal signal degradation).
One of the key benefits of RS-422 is its differential signaling. Instead of sending a signal on a single wire referenced to ground, it uses two wires. The difference in voltage between these two wires represents the signal. This clever trick makes it far more resistant to noise and interference. Think of it like listening to music with noise-canceling headphones; all that annoying background hum just fades away, leaving you with crystal-clear tunes. Similarly, RS-422 keeps the data stream clean and accurate even in electrically noisy environments. Pretty neat, huh?
RS-422 is often used in industrial settings, automation systems, and even some computer peripherals. Anywhere you need reliable communication over a reasonable distance, RS-422 is a strong contender. From controlling robotic arms in a factory to connecting scientific instruments in a lab, it's a workhorse that keeps things running smoothly. Think of it as the reliable plumbing system of the digital world; you might not see it, but you definitely notice when it's not working correctly!
So, we've established that RS-422 is a robust serial communication standard. But the big question remains: is it full-duplex? Lets unravel that mystery further.

Full-Duplex Unveiled
2. Diving Deep into Duplexity
Okay, buckle up, because we're about to talk about "duplexity." It sounds complicated, but it's really just about how communication happens. There are three main types: simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex. Simplex is like a one-way street; information only flows in one direction (think of a radio broadcast). Half-duplex is like a walkie-talkie; you can talk or listen, but not at the same time. Then there's full-duplex — the holy grail of communication — where you can talk and listen simultaneously, just like a phone conversation. Its the equivalent of having two separate lanes on a road, one going each way, allowing for smooth and uninterrupted flow of traffic.
The million-dollar question is, can RS-422 achieve this full-duplex nirvana? The answer is a resounding YES! RS-422 can indeed operate in full-duplex mode. However, and this is a crucial "however," it's not inherent in the RS-422 standard itself. The standard only defines the electrical characteristics and signaling methods. It specifies how the signals are transmitted, not necessarily how or when data is sent and received.
To achieve full-duplex communication with RS-422, you need a separate pair of wires for transmitting data and another pair for receiving data. Think of it as having two separate RS-422 channels operating independently. One channel is dedicated to sending information, while the other is dedicated to receiving. This setup allows for simultaneous, bidirectional communication, unlocking the full potential of full-duplex operation.
Think of it like this: RS-422 provides the reliable and noise-resistant foundation for communication, but full-duplex functionality is a separate "feature" that needs to be implemented on top of that foundation. It's like having a powerful engine in a car; it's got the potential for incredible speed, but you still need a separate accelerator and brake to control it effectively. Similarly, RS-422 provides the signaling, but the protocol and hardware configuration determine whether it's used in full-duplex mode or not.
![[DIAGRAM] Rs 422 Null Modem Cable Wiring Diagram [DIAGRAM] Rs 422 Null Modem Cable Wiring Diagram](https://ipc2u.com/upload/medialibrary/5d6/5d67f43941466633a7dc44bc48adc33f.jpg)
[DIAGRAM] Rs 422 Null Modem Cable Wiring Diagram
Wiring it Up
3. The Nitty-Gritty of Connections
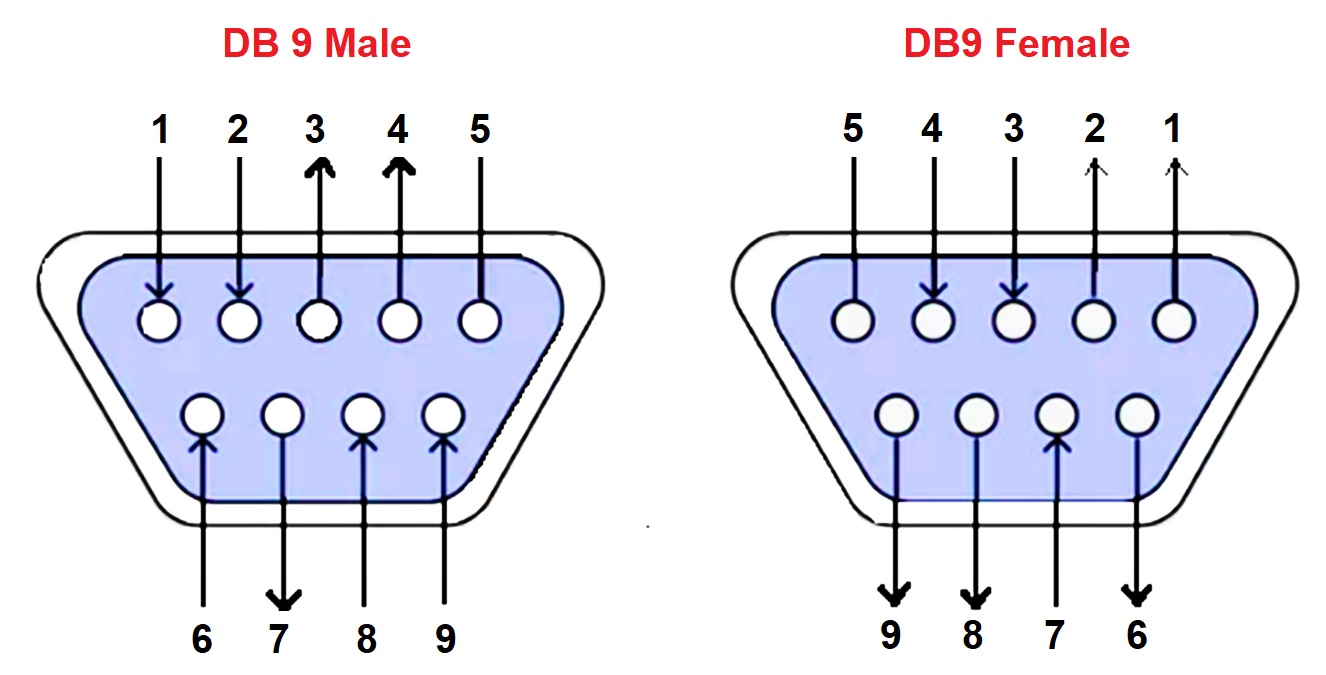
So, you're sold on the idea of full-duplex RS-422. Great! But how do you actually make it happen? Well, it all comes down to the wiring. Remember that you need two pairs of wires: one for transmitting (TX) and one for receiving (RX). Each pair uses differential signaling, meaning each signal has a positive (+) and a negative (-) wire. It's not rocket science, but getting the wiring wrong can lead to all sorts of headaches (and potentially fried circuits, so be careful!).
Typically, you'll find devices with RS-422 interfaces labeled with TX+, TX-, RX+, and RX- terminals. These labels clearly indicate the polarity and function of each wire. The key is to connect the TX+ and TX- terminals of one device to the RX+ and RX- terminals of the other device, and vice versa. This creates the two separate communication channels needed for full-duplex operation. If youre unsure, always consult the devices manual — its better to be safe than sorry!
It's also important to use proper cabling. Shielded twisted-pair cable is highly recommended for RS-422 applications, especially when running long distances or in noisy environments. The shielding helps to protect the signal from external interference, ensuring reliable communication. Think of it as wrapping your precious data in a protective blanket, keeping it safe and sound from all the electrical gremlins lurking around.
Finally, remember to terminate the RS-422 lines properly. Termination resistors are used at the ends of the cable to prevent signal reflections, which can cause data errors. Typically, a 120-ohm resistor is used for RS-422 termination. Implementing proper termination is crucial for maintaining signal integrity, especially at higher data rates. It's like putting shock absorbers on your car; it makes for a much smoother and more reliable ride. So, don't skip this step!

Real-World Applications
4. Putting it to Work
Okay, so we know how to do full-duplex RS-422, but why would you want to? Well, there are plenty of applications where simultaneous bidirectional communication is a huge advantage. Think about situations where real-time control and monitoring are critical, such as industrial automation, robotics, and high-speed data acquisition systems.
In a factory setting, for example, a robot might need to send sensor data back to a central controller while simultaneously receiving commands to adjust its movements. Full-duplex RS-422 allows for this continuous exchange of information, enabling precise and responsive control. It's like having a constant stream of feedback between the robot and its brain, ensuring everything stays in sync.
Another common application is in point-of-sale (POS) systems. Imagine a scenario where a cash register needs to send sales data to a server while simultaneously receiving price updates. Full-duplex RS-422 ensures that these transactions happen quickly and reliably, keeping the lines moving smoothly. Nobody wants to wait in a long line, so efficient communication is key.
Even in scientific instruments, full-duplex RS-422 can play a crucial role. For example, a spectrometer might need to send measurement data to a computer while simultaneously receiving commands to adjust its settings. This allows for real-time data analysis and control, enabling scientists to conduct experiments more efficiently. It's like having a direct line of communication between the instrument and the researcher, allowing for immediate feedback and adjustments.
Troubleshooting
5. When the Signal Fades
Even with the best planning, things can sometimes go wrong. When your full-duplex RS-422 system isn't working as expected, don't panic! There are a few common culprits to investigate. First, double-check your wiring. Make sure you've connected the TX and RX lines correctly, and that the polarity (+ and -) is correct. A simple wiring error can cause all sorts of problems.
Next, verify your termination resistors. Make sure they're the correct value (typically 120 ohms) and that they're properly connected at the ends of the cable. Incorrect termination can lead to signal reflections and data errors. Use a multimeter to measure the resistance across the termination points to ensure they match the expected value.
Another potential issue is cable length. RS-422 is designed for longer distances than RS-232, but there's still a limit. Exceeding the maximum cable length can result in signal degradation and communication errors. Check the specifications of your RS-422 transceivers to determine the maximum recommended cable length, and make sure you're not exceeding it.
Finally, consider the environment. Are there any sources of electrical noise nearby that could be interfering with the signal? Motors, generators, and other high-power equipment can generate significant electromagnetic interference (EMI). Try to route your RS-422 cables away from these sources, and consider using shielded cable to further reduce the impact of noise. A little detective work can often uncover the root cause of the problem, leading to a quick and effective solution.
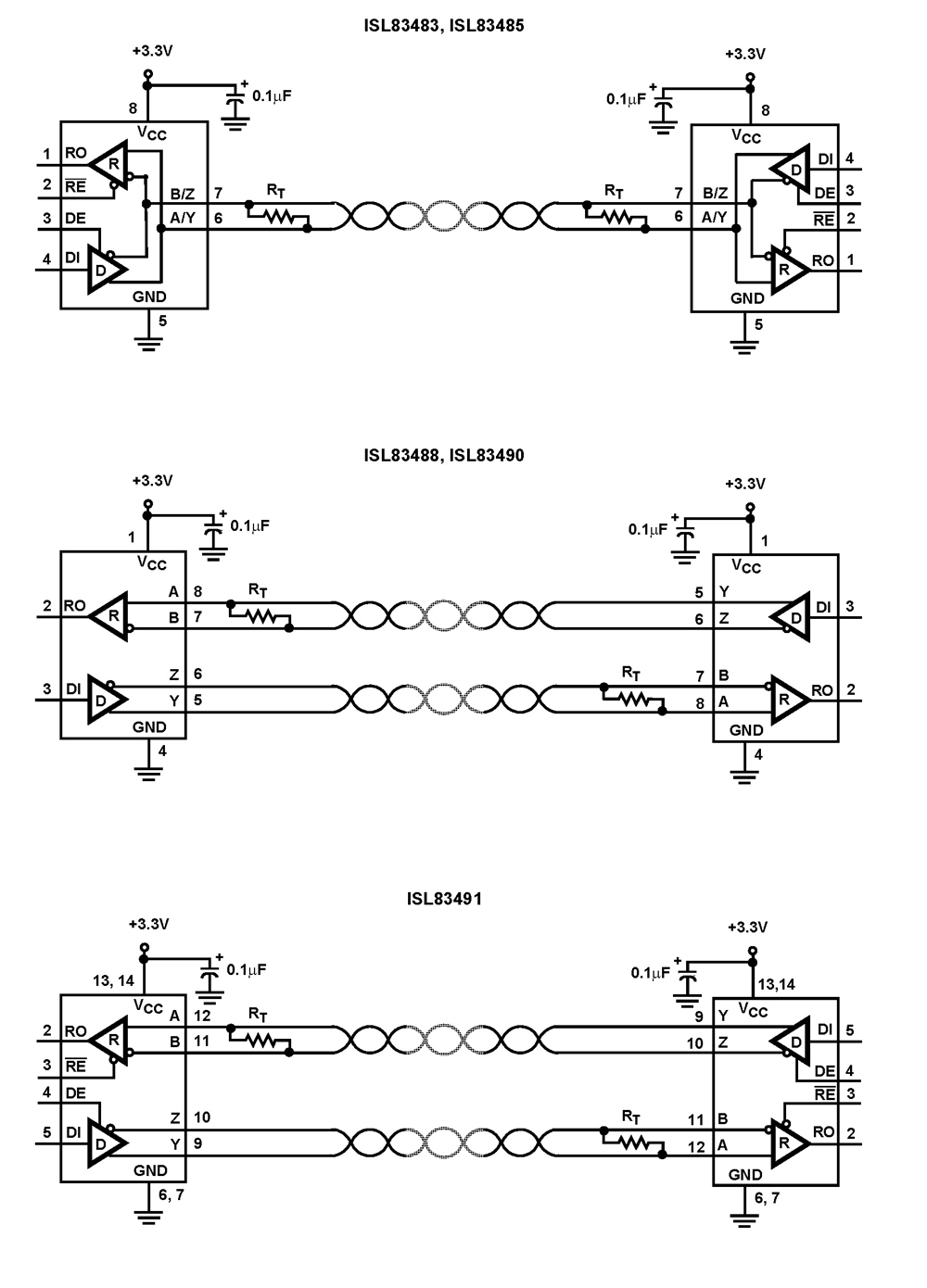
ISL83490 3.3V Full Duplex 10Mbps RS485/RS422 Transceiver Under
FAQ
6. Quick Answers to Common Questions
Still have questions about RS-422 and full-duplex communication? Here are a few frequently asked questions to clear up any remaining confusion:
Q: Is RS-422 better than RS-232?A: In many cases, yes. RS-422 offers longer communication distances, better noise immunity, and higher data rates compared to RS-232. However, RS-232 is simpler to implement and may be sufficient for short-distance applications with minimal noise.
Q: Can I use RS-422 with a USB port?A: Not directly. You'll need a USB-to-RS-422 converter to bridge the gap between these two interfaces. These converters typically handle the necessary signal conversion and protocol translation.
Q: What happens if I mix up the TX+ and TX- wires?A: If you reverse the polarity of the TX+ and TX- wires (or the RX+ and RX- wires), the communication may not work correctly, or you may experience data errors. Double-check your wiring to ensure that the polarity is correct.