Top Notch Info About Is All 3 Phase 400V

Understanding 3-Phase Power
1. Delving into Voltage Variations
So, you're pondering the world of 3-phase power and wondering if 400V is the only voltage you'll ever encounter? It's a great question! Think of it like asking if all cars are the same model. They all get you from point A to point B, but there are definitely differences under the hood — and in the voltage levels, too.
The short answer is no, not all 3-phase systems operate at 400V. While it's a very common voltage in many parts of the world (especially Europe), it's not a universal, one-size-fits-all standard. Imagine showing up to a party expecting pizza and finding sushi instead. Both are great, but they're definitely not the same thing! Different regions and applications use different voltage levels based on historical reasons, infrastructure development, and specific needs.
You might find different voltages in industrial settings versus residential areas. Think about a massive factory with heavy machinery versus a small office building. The factory likely needs a much higher voltage to power its equipment efficiently. This is because higher voltage allows for lower current to deliver the same amount of power, reducing losses in the power lines. Just like using a wider pipe to move more water with less resistance.
And just when you thought you had it figured out, regulations and standards also play a crucial role. National and international standards bodies set guidelines for voltage levels to ensure safety, compatibility, and efficiency. These standards can vary from country to country, making it even more important to know what voltage your equipment is designed for before plugging it in. Imagine trying to fit a square peg into a round hole; it's just not going to work!
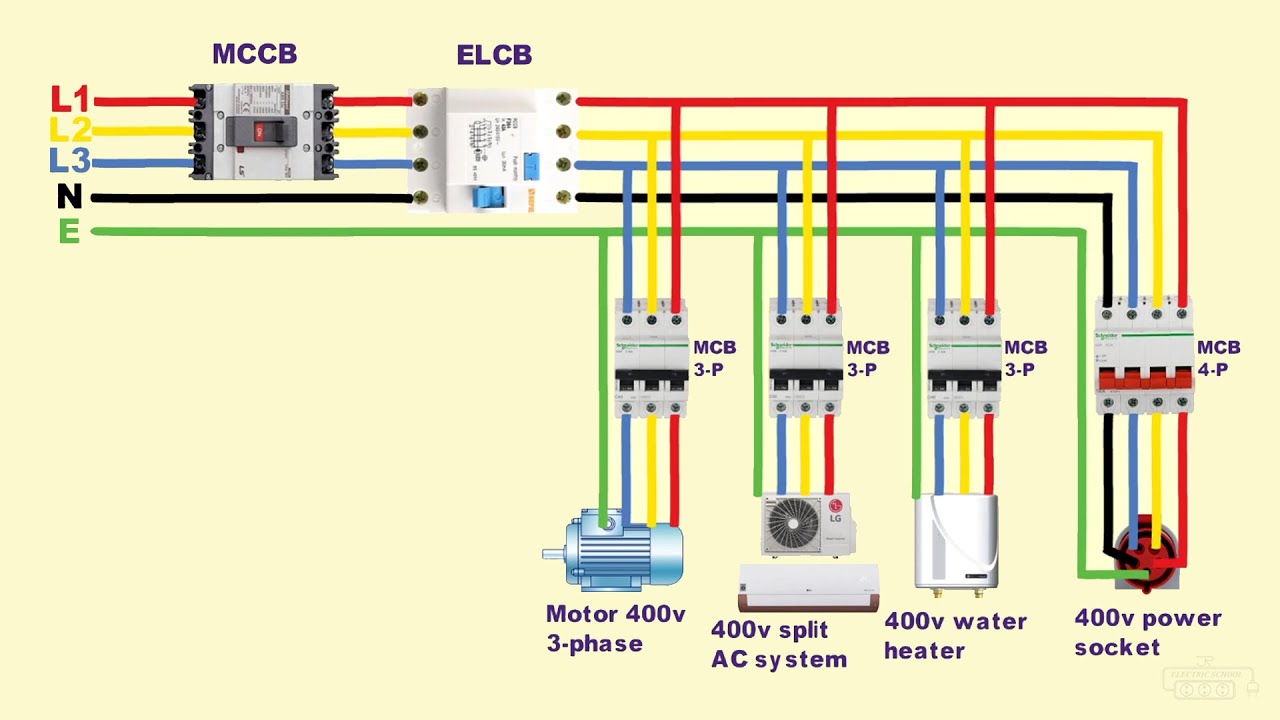
Q7) A Threephase, 400V, 50Hz, Fourpole, Yconnected Induction Motor
Why 400V is So Common (But Not Everywhere)
2. The Rise of 400V's Popularity
So, if it's not universal, why is 400V so prevalent, especially when talking about 3-phase systems? Well, it's kind of like the "popular kid" in the voltage playground. It strikes a good balance between safety, efficiency, and practicality for a wide range of applications.
Primarily, 400V provides a sweet spot for powering industrial machinery, commercial buildings, and even some residential installations. It's high enough to minimize current and reduce energy losses during transmission, yet low enough to generally avoid the need for extremely specialized and expensive equipment. Think of it as the Goldilocks zone of voltage: not too high, not too low, but just right!
Another reason for its popularity is historical precedent, particularly in Europe. Over time, 400V (or the related 230V single-phase) became the standard voltage for many countries due to a combination of historical infrastructure development and standardization efforts. It's simply been built into the electrical grid for decades, and changing it now would be a massive undertaking. Like trying to change the direction of a river, it's a difficult and costly process.
Furthermore, equipment manufacturers have responded to this prevalence by designing and producing a wide range of 400V-compatible devices, making it easier and more cost-effective for businesses and consumers to adopt. It creates a positive feedback loop: the more common the voltage, the more equipment is available, and the more appealing it becomes. This makes it similar to a popular language, as more resources available makes it easier to learn and use.
Voltage Variations Across the Globe
3. A World Tour of Electrical Voltages
Okay, let's take a quick trip around the world to see what other voltages are out there! Just like different countries have different languages and currencies, they also have different electrical systems. You'll find a variety of 3-phase voltage standards depending on where you go.
In North America, for example, you'll often see 208V, 480V, and even 600V 3-phase systems, particularly in industrial and commercial settings. These voltages have their own historical reasons and are still widely used today. It's like seeing different types of architecture depending on the region; each one has its own story.
Even within Europe, there can be slight variations. While 400V is the nominal voltage, some countries might have systems that operate slightly above or below this level. It's essential to check the specific requirements of your location before connecting any equipment. Like needing a specific adapter for different types of outlets when you travel.
The takeaway is that you can't simply assume that 400V is the standard everywhere. Always check the local regulations and equipment specifications to ensure compatibility and avoid any electrical mishaps. Failing to do so can be similar to using the wrong type of fuel in your car, you might end up with big problems!
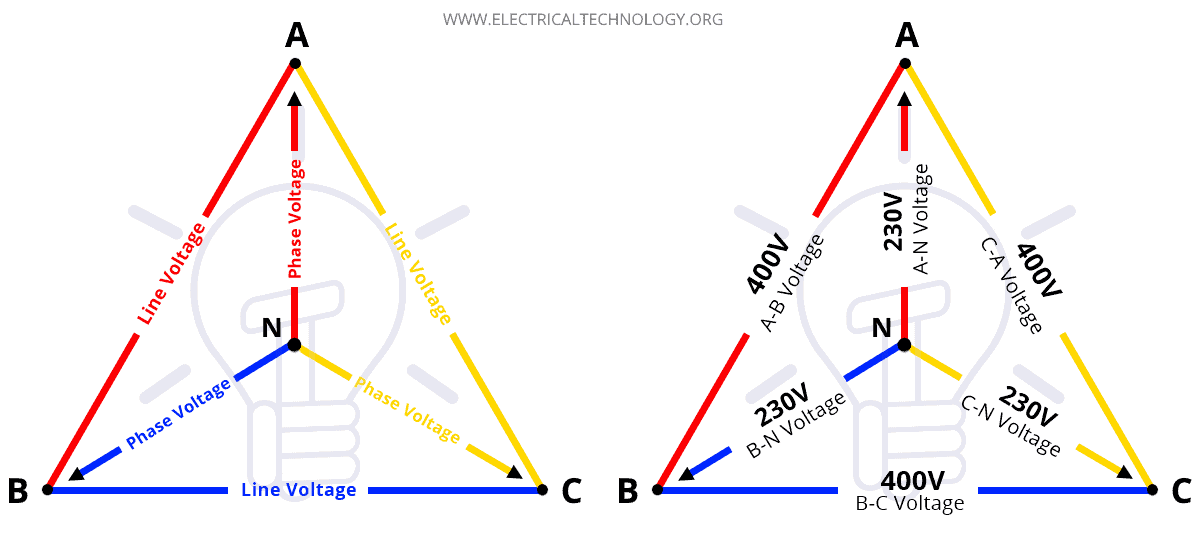
If A 1Phase Supply Is 230V, Why 3Phase 400V & Not 690V?
Why Correct Voltage Matters
4. The Importance of Voltage Matching
Using the correct voltage is crucial for the safety and proper functioning of electrical equipment. Think of it like prescribing the right dosage of medicine — too little, and it won't work; too much, and it can be harmful.
Applying the wrong voltage can lead to a variety of problems, ranging from reduced performance and efficiency to complete equipment failure and even fire hazards. Undervoltage can cause motors to overheat and burn out, while overvoltage can damage sensitive electronic components. Imagine trying to run a marathon with too little or too much water; you're not going to perform at your best, and you might even collapse.
Therefore, it's essential to check the voltage rating of your equipment and ensure that it matches the voltage of the power supply. If they don't match, you'll need to use a transformer to step up or step down the voltage to the appropriate level. It's like using a translator when you're speaking to someone who doesn't understand your language, it allows you to communicate effectively.
Proper voltage matching not only protects your equipment but also ensures the safety of personnel. Electrical accidents can be serious, and using the wrong voltage can increase the risk of shocks, burns, and even electrocution. Don't take any chances when it comes to electricity; always double-check the voltage and follow safety guidelines. Electrical safety should be prioritized over any other considerations.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About 3-Phase Voltage
5. Your Questions Answered
Let's tackle some common questions people have about 3-phase voltage. Consider this the FAQ section of our electrical adventure!
6. What happens if I connect 230V equipment to a 400V supply?
It's generally a bad idea to directly connect 230V equipment to a 400V supply. It will likely result in damage to the equipment, potentially causing it to overheat, smoke, or even catch fire. You would need a step-down transformer to reduce the voltage from 400V to 230V. Treat electricity with respect, and don't take shortcuts that could lead to dangerous situations.
7. How do I identify the voltage of a 3-phase power supply?
The voltage of a 3-phase power supply is typically indicated on a label near the main breaker or distribution panel. It might also be listed in the electrical documentation for the building or equipment. If you're unsure, it's best to consult a qualified electrician. When in doubt, always seek expert assistance, just as you would consult a doctor for medical advice.
8. Can I convert single-phase power to 3-phase power?
Yes, it is possible to convert single-phase power to 3-phase power using a rotary phase converter or a static phase converter. However, these converters can be expensive and may not be suitable for all applications. Consult an expert to determine the best solution for your specific needs. Before undertaking any complex electrical work, make sure you are well-informed and prepared.
